Understanding and Using Phenomenon Based Learning + Infographic
Phenomenon Based Learning uses the 3D NGSS framework, which utilizes SEPs, CCCs, and DCIs to help students achieve mastery in science. Feeling overwhelmed yet?
Wait!
Do not run away screaming. It’ll be okay.
Check out the images and the simple explanations of what it’s all about below.
While phenomena can be used as starting points for lessons in multiple subjects, not just science, this article explains how Phenomenon Based Learning (PhenBL) fits with the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS).
However, NGSS were written to emphasize the idea that students should be developing skills while learning subject content. Many of these skills - asking questions, defining problems, obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information, and engaging in argument form evidence, to name a few - can be used across most disciplines.
Traditionally, science teaching has focused on students being presented concepts by teachers and then using those concepts in labs and activities and proving their knowledge of these concepts on tests.
Phenomenon Based Learning used with NGSS aims to provide the missing connection between concepts learned in class and the world at large. By using a phenomenon at the beginning of a lesson, or a unit, teachers push students to undertake a journey of discovery - a journey that leads to students discovering on their own why and how this phenomenon happens, and in the process, they learn the content and skills described by the NGSS.
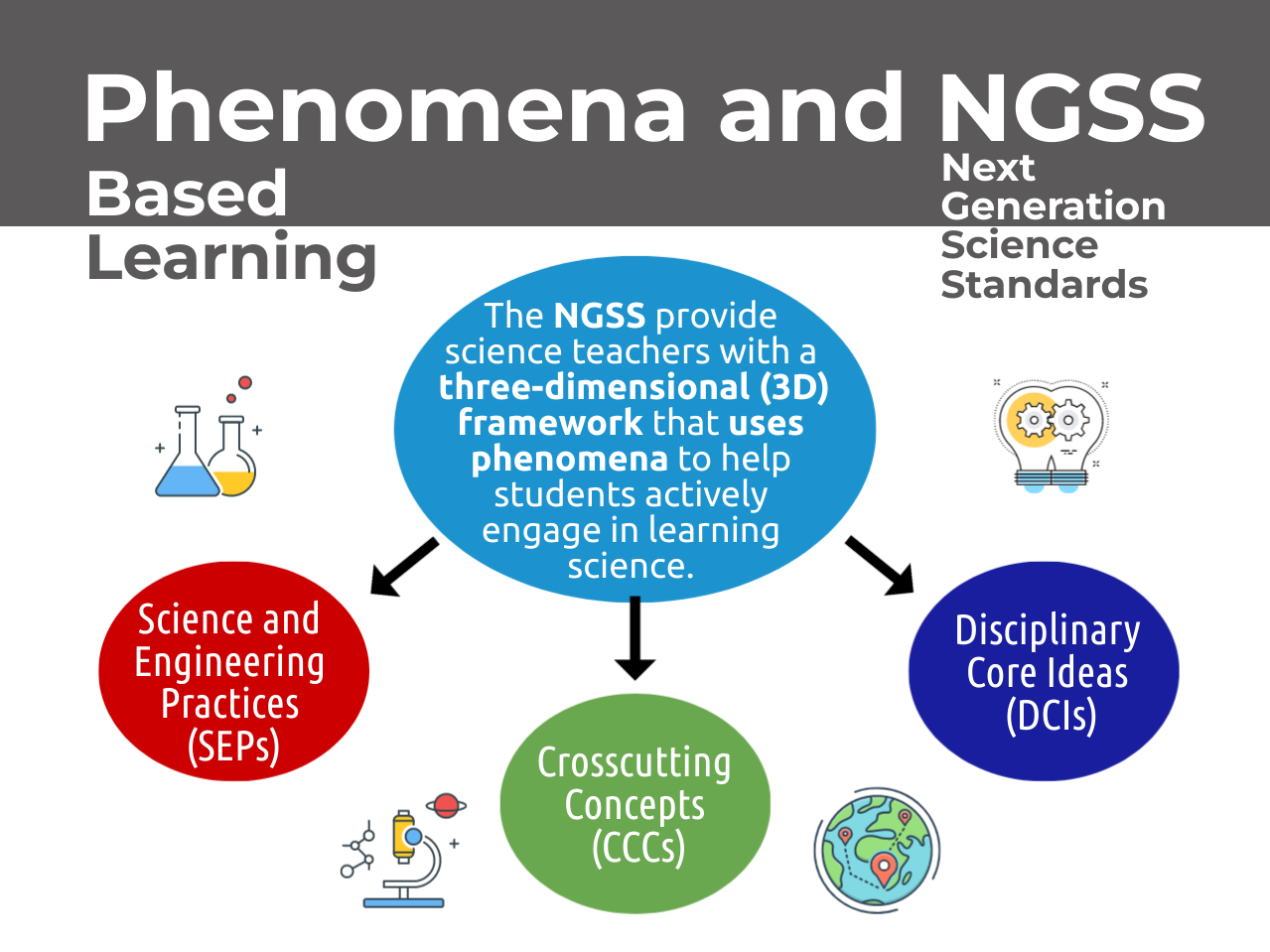
NGSS aims to use Phenomenon Based Learning to achieve 3D Learning.
When students are not spoon-fed concepts up front, but asked to investigate on their own instead, they use (guided by teachers) skills - called Science and Engineering Practices (SEPs), encounter Crosscutting Concepts (CCCs), and learn Disciplinary Core Ideas (DCIs).
Thus, when NGSS uses the term three-dimensional, or 3D Learning, it refers to the three components - SEPs, CCCs, and DCIs - which will be explained in some detail below.
The big idea (and hope) is that PhenBL will give students the opportunity to use and learn these three components as they investigate and solve the phenomena.
Let’s examine each 3D framework component one by one.
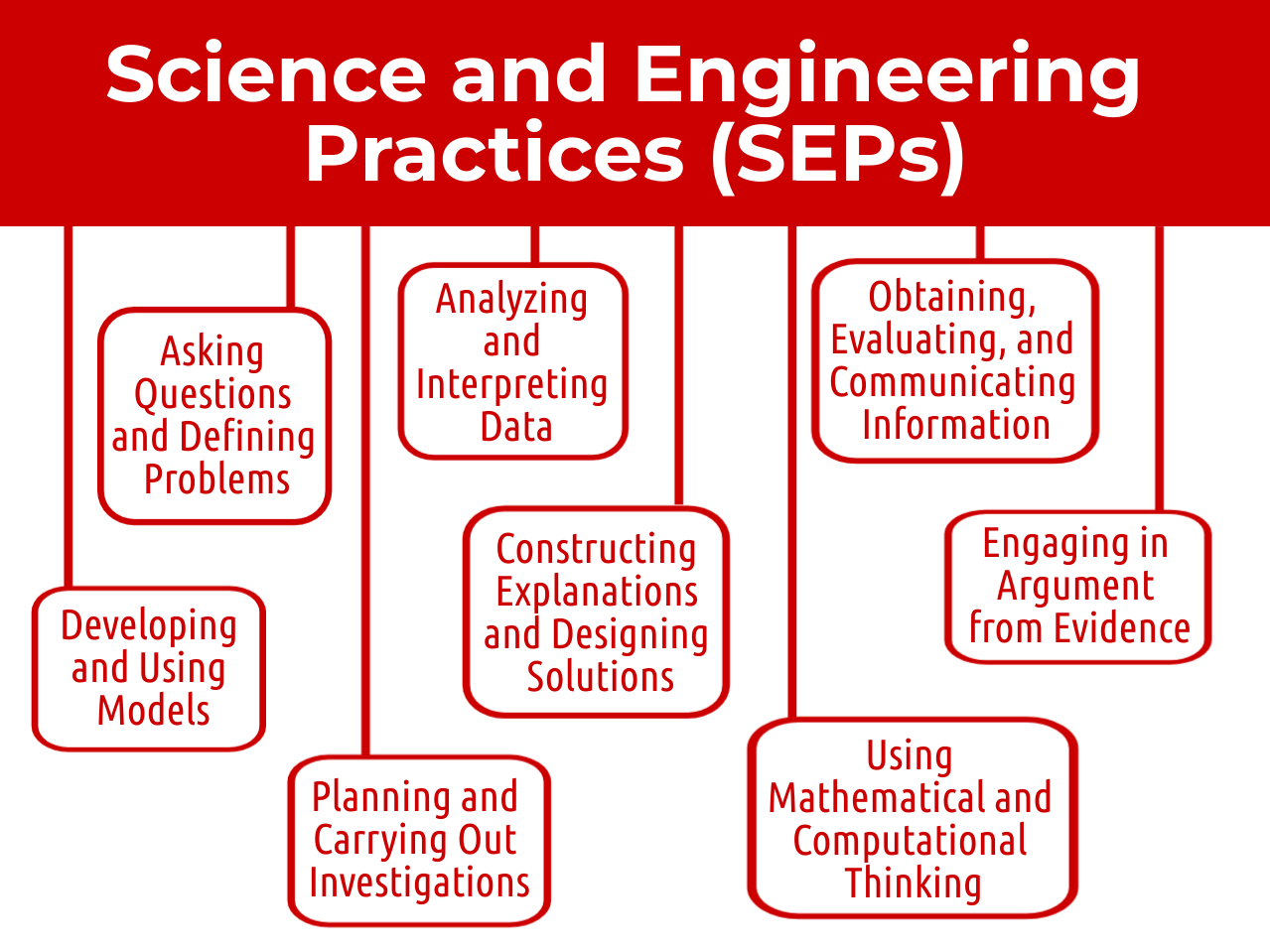
Science and Engineering Practices (SEPs) can be described as thinking, design, and communication skills.
Science and Engineering Practices (SEPs) can be described as thinking, design, and communication skills the NGSS team hopes students hone as they investigate various phenomena presented to them.
Students are not expected to use all of the SEPs all of the time. Rather, multiple (but not all) skills are utilized and improved during investigations into the phenomena.
Repeated exposure is key, so creating multiple PhenBL lessons throughout the school year and the continued teacher guidance during student explorations will lead to higher quality thinking, design, and communication skills.
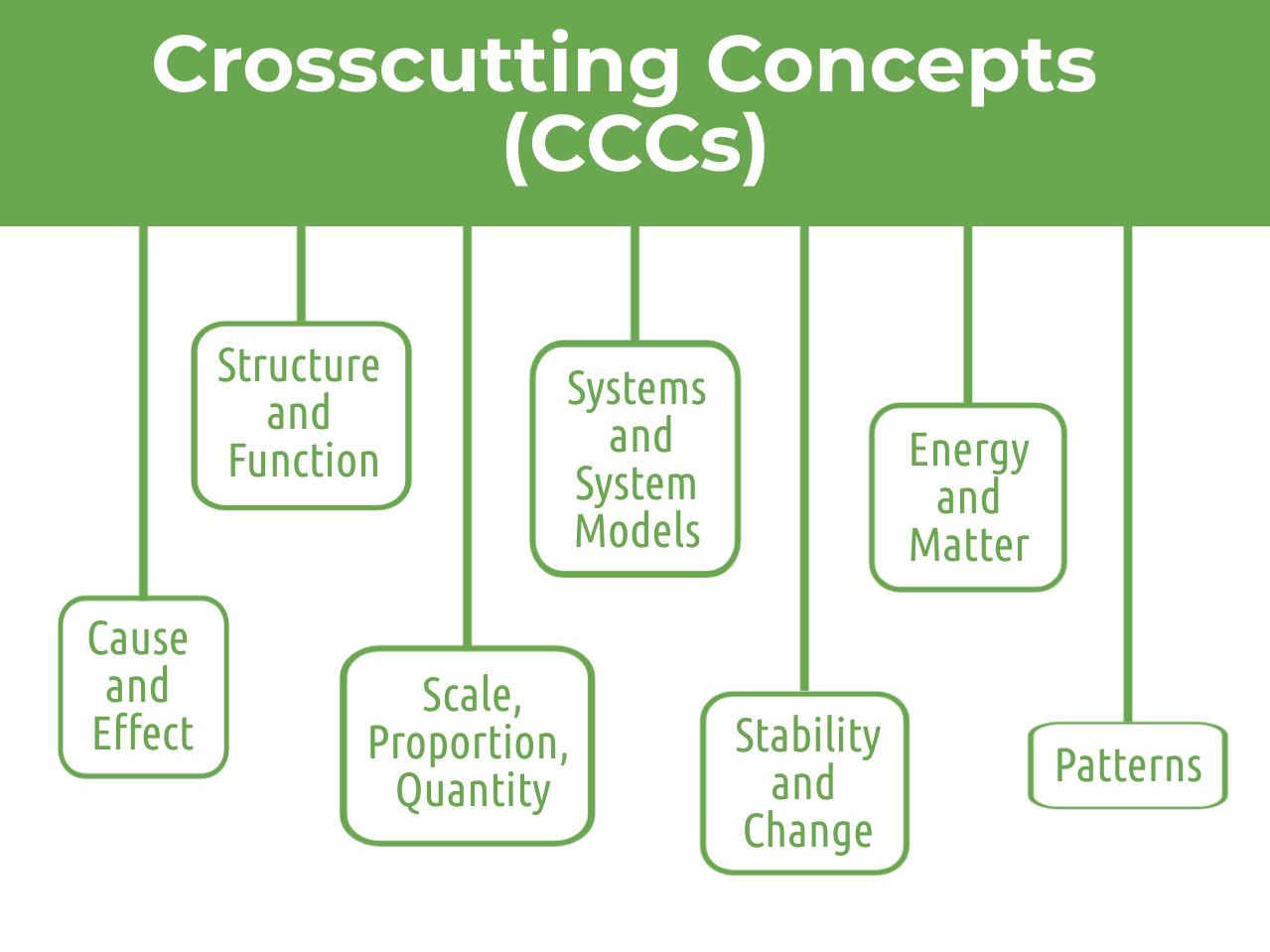
Crosscutting Concepts (CCCs) can be thought of as tools to be used when creating explanations and models.
Disciplinary Core Ideas (DCIs) are the main concepts that connect the four core science disciplines.
Crosscutting Concepts (CCCs) can be thought of as the tools students can use when communicating explanations of observed phenomena and constructing models that explain the core concepts that cause these phenomena to occur.
They are “crosscutting,” because they provide ways to connect the four core science disciplines and each of these disciplines makes use of them when explaining interactions of matter and energy in various living and nonliving systems.
The Disciplinary Core Ideas (DCIs) are the main concepts that connect the four core science disciplines: Earth and Space Science, Engineering and Technology, Physical Science, and Life Science.
Phenomenon Based Learning provides a path for students to develop a deep understanding of DCIs. First, students encounter the fundamental concepts in the scientific discipline they are studying. Subsequent attempts at solving a phenomenon lead to connecting these core concepts to the core concepts from other disciplines. Then, these understandings can be put together to create the big picture - how the world at large works.
Bringing focus to the big picture takes multiple investigations across multiple disciplines across many years of schooling. The job of any teacher then, is to provide students with many opportunities to build the skills and the knowledge base that will ultimately allow students to formulate not just a good understanding of the planet they live on, but also will give them the capability to use Earth resources intelligently and make decisions that benefit humanity now and in the long term.
Did you find this post helpful? The next one, Where and How to Begin with Phenomenon-Based Learning, will talk about how to plan a PhenBL lesson so students learn the required content. Sign up for my Teaching Tips, Resources, & Ideas Newsletter to get it when it drops. It’s totally free.
But, If you’d like a copy of the graphics featured in this post, they are available as a long form, high quality, full size infographic for $5 here ———————————————>
BOOKS & TOOLS
- September 2025 2
- August 2025 5
- July 2025 4
- June 2025 2
- August 2024 2
- July 2024 2
- June 2024 1
- October 2023 1
- September 2023 3
- August 2023 6
- July 2023 6
- July 2022 2
- June 2022 1
- November 2020 3
- October 2020 3
- April 2020 1
- March 2020 5
- July 2019 1
- June 2019 1
- April 2019 1
- January 2019 1
- November 2018 3
- October 2018 2
- September 2018 1
- August 2018 8
- July 2018 11
- June 2018 4
- May 2018 5
- April 2018 2
- March 2018 4
- February 2018 5
- January 2018 3
- December 2017 1
- November 2017 5
- October 2017 7
- September 2017 6
- August 2017 5
- July 2017 3
- June 2017 10
- May 2017 7
- April 2017 7
- March 2017 15
- February 2017 12
- January 2017 13
- December 2016 15
- November 2016 8
- October 2016 7
- September 2016 12
- August 2016 14
- July 2016 10
- June 2016 13
- May 2016 10
- April 2016 8
- March 2016 5
- February 2016 7
- January 2016 6
- December 2015 5
- November 2015 8
- October 2015 2